Electric Camping Coolers: Types, Power Usage, and Solar Panel Sizing
This page contains affiliate links, and that means that I may earn a commission if you buy something, at no extra cost to you. You can find my full disclosure policy here.
What Is an Electric Camping Cooler?
An electric camping cooler is a portable refrigeration appliance powered by 12V DC, 24V DC, or 110–240V AC electricity.
The unit maintains internal temperatures from -22°C to +20°C without ice.
Electric camping coolers rely on active heat transfer rather than passive insulation.
Primary cooling mechanisms
- DC compressor refrigeration
- Thermoelectric (Peltier) heat transfer
What Types of Electric Cooler Technologies Exist?
Compressor-Based Electric Coolers (DC Refrigerator Systems)
A compressor cooler uses a vapor-compression refrigeration cycle.
It maintains stable internal temperatures regardless of ambient heat.
How the system works
- A brushless DC compressor compresses refrigerant
- A condenser expels heat externally
- An evaporator absorbs heat internally
Key technical attributes
| Attribute | Specification |
|---|---|
| Compressor brands | Secop, LG |
| Cooling range | -22°C to +10°C |
| Freezing capability | Yes |
| Dual-zone support | Yes |
| Average draw | 0.7A–1.5A |
| Insulation | Rotomolded HDPE |
| Wall thickness | 50 mm or more |
Measured performance
The Dometic CFX3 45 averages 0.87 Ah/h at 32°C ambient temperature under steady-state conditions.
Use case
You choose compressor coolers for:
- Off-grid camping
- Overlanding vehicles
- Solar-powered systems
- Food-safe refrigeration above 30°C ambient
Thermoelectric coolers (Peltier effect)
A thermoelectric cooler transfers heat using the Peltier effect.
Electric current moves heat from the cold plate to the hot plate.
Key technical attributes
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Cooling delta | 18–20°C below ambient |
| Freezing capability | No |
| Moving parts | None |
| Weight | Low |
| Cost | Low |
| Runtime | Continuous |
| Hot climate efficiency | Low |
Thermal limitation
A Peltier system cannot maintain food-safe temperatures when ambient air exceeds 30°C.
Practical implication
You use thermoelectric coolers for:
- Short trips
- Mild climates
- Beverage cooling
How much power does a 12V electric cooler use per day?
Step-by-step energy calculation
You calculate daily consumption using measured electrical load.
Calculation method
- Measure average amp draw
- Multiply by compressor duty cycle
- Convert to daily amp-hours
Typical real-world values (2026)
| Parameter | Range |
|---|---|
| Average draw | 0.7–1.5A |
| Duty cycle | 25–35% |
| Daily consumption | 30–50Ah |
Independent testing from 12 Volt Blog
After testing, the data shows 30–50L compressor fridges average 35Ah/day at 25°C ambient.
Environmental factors affecting power draw
Direct impact variables
- Higher ambient temperature → higher duty cycle
- Poor airflow → longer compressor runtime
- Thin insulation → increased heat gain
- Frequent lid openings → thermal loss
Battery Optimization rule
Set the internal temperature to 3°C if you want to minimize battery depletion while maintaining food safety.

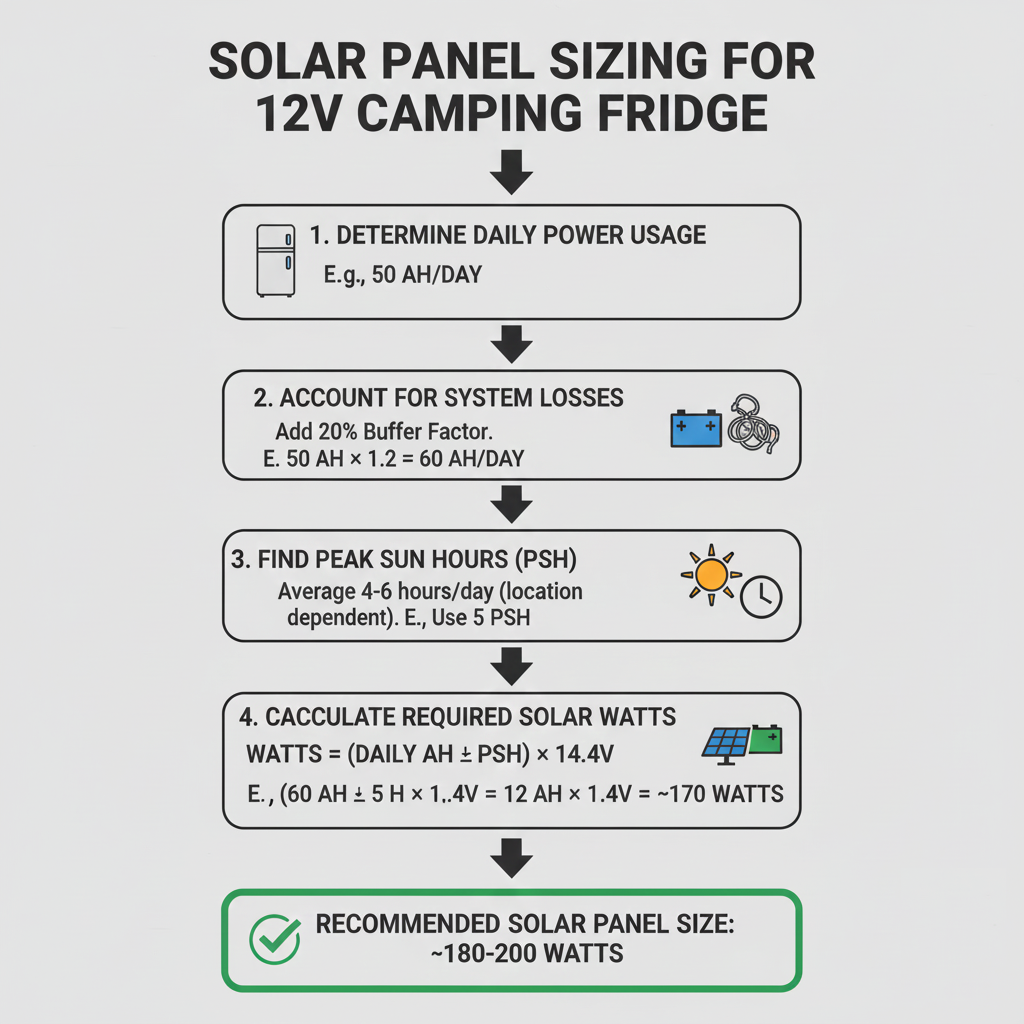
How do you calculate solar panels for a 12V camping fridge?
Core factual proposition
A 100W solar panel produces 400–500Wh per day under 5 peak sun hours.
Panel sizing equation
Daily Wh ÷ Peak Sun Hours × 1.25 = Minimum Panel Size
| Input | Value |
|---|---|
| Daily fridge usage | 500Wh |
| Peak sun hours | 5 |
| Buffer factor | 1.25 |
Example calculation
Result
500 ÷ 5 × 1.25 = 125W solar panel
You oversize panels if:
- You camp in high heat
- You run the fridge 24/7
- You rely on solar only
What connectivity and battery protection features matter? (2026)
Control and monitoring features
Modern electric coolers include:
- Bluetooth 5.0 app control
- Real-time Wh consumption tracking
- Temperature curve logging
Electrical safety and battery protection
Integrated safeguards
- Low-voltage cut-offs
- AGM and LiFePO compatibility
- Automatic compressor throttling
These systems prevent battery over-discharge during extended off-grid use.
